Shark Products – What They Are and Their Journey
Explore what types of shark products are used, how demand has changed over time, and the way in which they move from origin to consumer.
Introduction
The "State of the Global Market for Shark Products" report published by the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations in 2015 is a goldmine of information about the flow of trade in shark and ray products around the world. This interactive infographic brings to light the key findings of the report. It visualizes the complex, global and interdependent market for shark and ray meat and fins. We hope you’ll gain valuable insights into the complexity and be inspired to help protect sharks and rays from overfishing.
What are shark* products?

Generally, larger fins are more valuable than small ones, but all sizes enter trade.


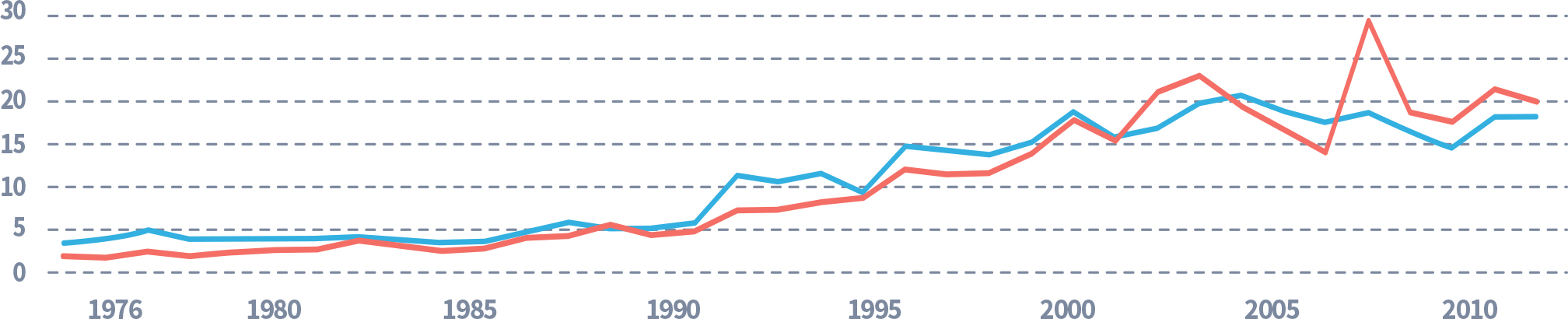
Demand for Shark fins

The annual volume for fin imports decreased from 17,682 tonnes (t) in 2000 to 16,815 t in 2011.
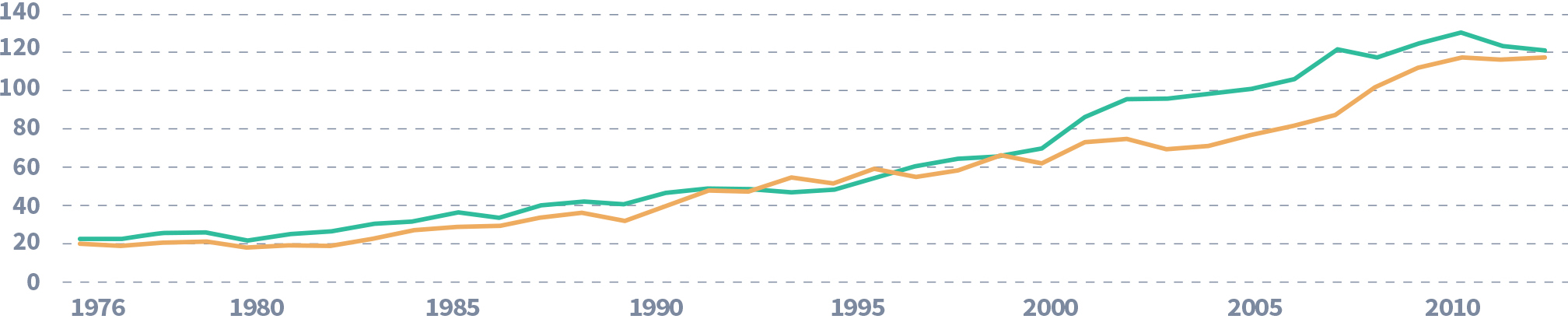
Demand for Shark Meat
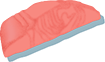
In 2011, the annual volume for shark (including skate and ray) meat imports was 121,641 t compared to 85,710 t in 2000.
A complex supply chain
produced (separated from carcass)
to a regional trader.
regional trader

processing
center (processed again)
consuming country


Shark products are often imported and exported more than three times.
trends in trade: 1976-2011